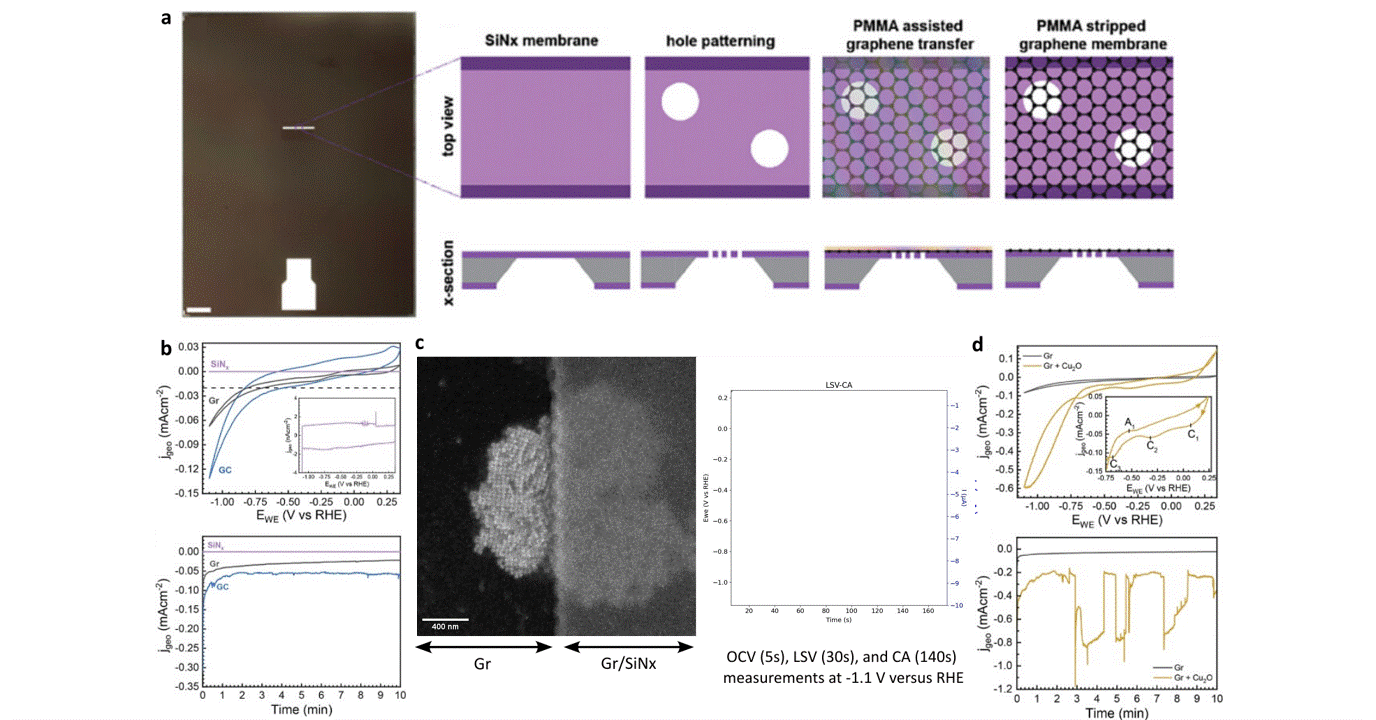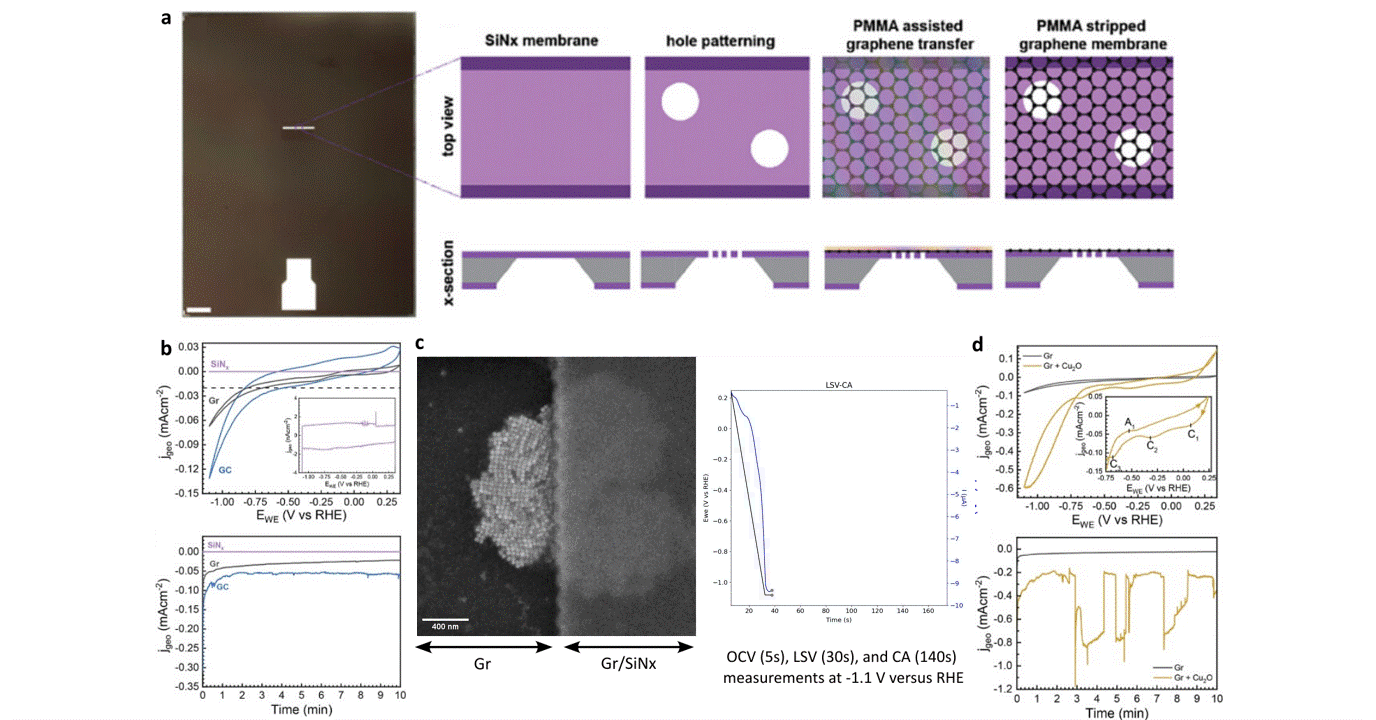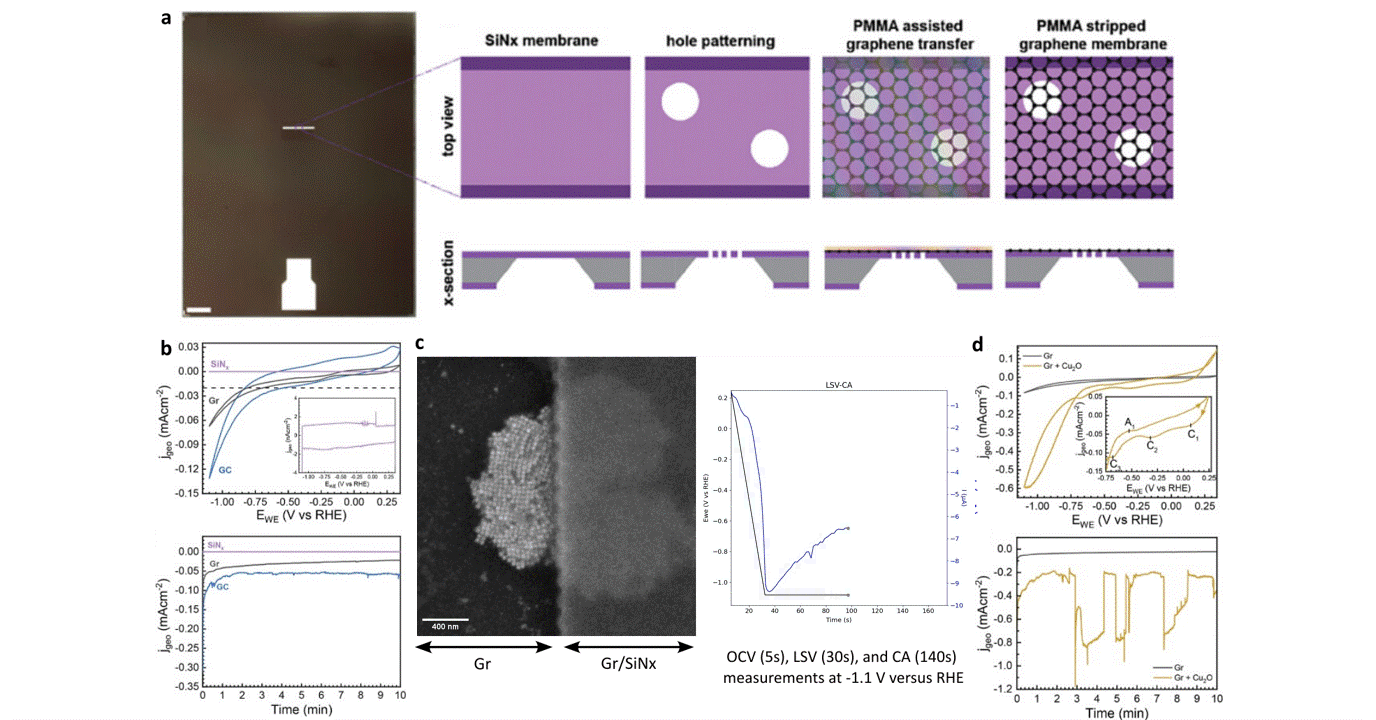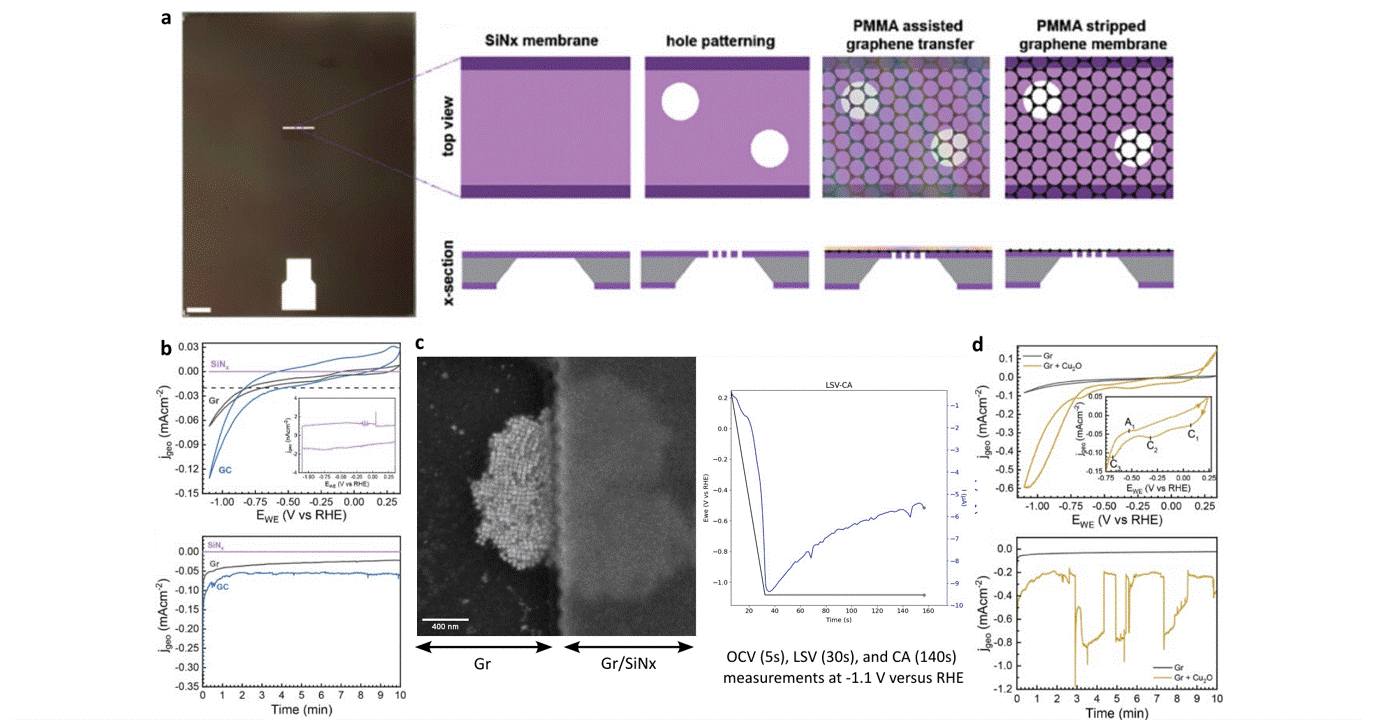
Operando liquid electrochemistry using graphene membrane working electrode
Researchers at EPFL published recent work characterizing graphene as a working electrode for CO2 electroreduction (CO2ER) of Cu nanocatalysts with the Hummingbird Scientific Generation V bulk liquid-electrochemical SEM system. The robust three-layer graphene membrane, which served as the sample carrier, working electrode, and liquid sealing membrane, was applied to the chip via a wet transfer process. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) plots indicated a wider inert cathodic range for the graphene working electrode than glassy carbon. Keeping the probe current low enabled imaging of nanocube degradation and secondary particle deposition during CO2ER at operating potential of -1.1 V vs RHE.
Figure: a) Schematic of graphene membrane preparation via wet transfer process. b) Cyclic voltammetry (CV) and chronoamperometry (CA) of SiNx, graphene, and glassy carbon comparing performance and inert potential range. c-d) Operando SEM, voltammetry and amperometry for CO2ER of Cu nanocatalysts.
Image Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Advanced Materials published by Wiley-VCH GmbH
Reference: Toleukhanova et. al. Adv. Mater. 36 (16) 2311133 (2024) DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c09105